Lea esta historia en español aquí.
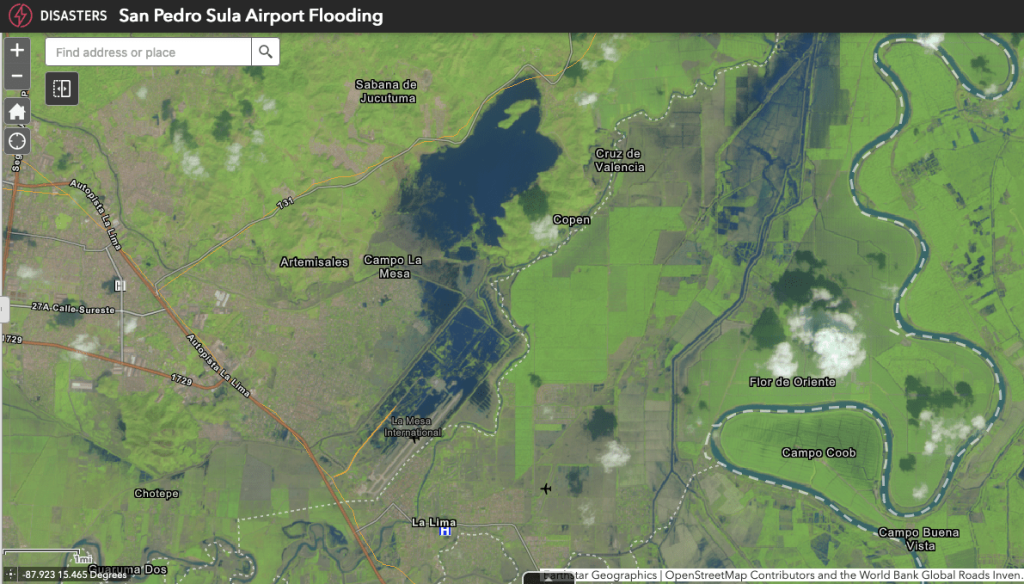
Shortly after Category 4 Hurricane Iota began to drench Central America on Nov. 16, 2020, Claudia Herrera watched from a helicopter as ruinous flood water inundated entire neighborhoods of La Lima, in Honduras’ Valley of Sula. In just three days, the catastrophic rainfall of Iota had flooded Ramon Villeda Morales International Airport in La Lima, as well as schools, healthcare centers, and other critical infrastructure in a region that serves as the country’s main economic engine.
The view from the helicopter was too familiar for Herrera, who leads the Coordination Center for Disaster Prevention in Central America, or CEPREDENAC for its acronym in Spanish. Two weeks earlier, Category 4 Hurricane Eta had battered the region, with Honduras bearing the brunt of the storm’s cataclysmic force. Herrera had been helping regional authorities plan their response to the storms’ destructive winds and heavy rain, which had also scarred important mangroves in Nicaragua and triggered deadly landslides in Guatemala.
Soon after Eta touched down in northern Nicaragua on Nov. 3, NASA’s Earth Applied Sciences Disasters program area began working with Herrera and other authorities in Central America to use satellite images and data to monitor damage and help teams on the ground analyze the affected terrain as they rescued people affected by the storm.
As thousands of people within and beyond the region joined forces to help, the impending impact of a second, virtually “twin” storm shocked everyone. Iota was going to make landfall within 20 miles of where Eta had.
“When we were warned about Iota, and we sent this information to the local authorities, we could not believe it—that it was possible that another storm was coming, and that it was going to affect us with the same magnitude almost simultaneously,” Herrera said. “We had not finished making damage reports, quantifying the damage of Eta’s impact, when we were already bracing for Iota’s impact.”
Eta destroyed highways connecting the Sula Valley to the rest of the country, adding another layer to the challenge of providing humanitarian support to people in need and creating a feeling of helplessness, Herrera said. The massive, coordinated efforts to help displaced communities find shelters took the help of everyone in the country—and beyond.
Teams flew in from the United States and Colombia to assist Honduran armed forces leading the way. Local partners in the private sector also provided helicopters and equipment. Local fishermen helped people trapped by floods in tight areas in their own small fishing boats. Remotely, NASA’s Disasters program provided products updated on a near real-time basis for teams on the ground.
The ability to operate nimbly while coordinating information transfer with NASA’s help was crucial for the team’s efforts as it helped the region connect with other geospatial organizations that also provided support, said Marcelo Oyuela, the lead geographic information systems engineer of the Central American organization.
“Sometimes there is a lot of data and information, but the knowledge that is missing is where that information is, where those initiatives are,” Oyuela said.
An Abundance of Storms
In unusually quick succession, Eta and Iota capped a disastrous hurricane season for Central America, which had not been hit as badly since Category 5 Hurricane Mitch in 1998. The storms contributed to a season that marked the fifth consecutive year with hurricane activity well above average.
Although the abundance of storms in 2020 does not guarantee hurricanes will become more frequent in the coming years, scientists say ocean warming is already changing hurricane behavior and expect that ocean warming will fuel more intense hurricanes in the future.
When Eta and Iota passed over the Caribbean’s warm waters, their wind speed increased drastically in under 36 hours as a result of a rapid intensification phenomenon scientists expect to become more common as ocean temperatures rise.
For the past few decades, hurricanes have been rapidly intensifying more often, and their forward motion has been stalling more, dropping more rainfall over confined locations. Eta, Iota and other major hurricanes contributed to that trend in 2020, which saw a record-tying nine storms intensify rapidly. These quick changes in storm strength can leave communities in their path without time to properly prepare.
“There’s no observed trend globally on the frequency of storms. Some years and some ocean basins have more and then less,” Tim Hall, a hurricane researcher at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York, told NASA’s Earth Observatory in 2020. “But if you already have a hurricane formed, we have found that global warming signals are increasing a storm’s likelihood to stall, intensify into a major hurricane, and drop more rain.”
Eta and Iota also formed well past the time of year when major hurricane activity is expected to peak. As ocean and atmospheric temperatures continue to rise, major storms late in the season will likely become more common. The hurricane season officially runs from June 1 to November 30, and by early August, the Atlantic Ocean is primed for hurricanes.
A Global View for Regional Resilience
NOAA has predicted another highly active season for 2021. In Honduras, Herrera also expects a taxing season because of the damage and fear that lingers.
Herrera’s team continues to work closely with NASA’s Disaster program and other international government agencies and private groups. Their initiative is fully focused on strengthening resilience for each country in the region.
“Right now, there are already four countries affected with flooding—Honduras, Guatemala, Nicaragua and Panama—without even having entered the season of significant storms,” Herrera said in June. “We are taking all possible measures to prepare for this rainy season, but we have a very big challenge with the impact of hurricanes Eta and Iota still in the territory.”
In 2020, there were a record-breaking 30 named hurricanes in the Atlantic, and scientists are tracking how human-caused climate change is altering storm behavior. NASA monitors hurricanes from space using Earth-observing satellites, and we feed that data to weather models to better our understanding of a hurricane’s trajectory and magnitude.
Credits: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Scientific Visualization Studio
Because other agencies also aid in response and recovery work after storms like Eta and Iota hit, the work of the Disasters team always requires a tremendous amount of coordination with local and international groups to streamline the flow of information.
One of the program’s priorities focuses on partnering with local and international groups to generate data-based products with a global view of Earth and applying that information down at the regional level, said David Green, who manages the program.
“We seek to develop trusted relationships within a cultural context with vulnerable communities and those able to take action, which means we bring in population data, we bring in economic information, we reach out to those at risk, as well as partners in humanitarian relief, including the Bureau of Humanitarian Affairs of USAID, the UN disaster groups in Panama, the mapping groups in Costa Rica, and the satellite agencies in Mexico,” Green said. “We collect that knowledge because we’ve learned to engage the village to build sustainable resilience.”
View the products the NASA Disasters team prepared for Hurricanes Eta and Iota in 2020.
Download this video from NASA Goddard’s Scientific Visualization Studio.
By Roberto Molar Candanosa
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Hurricanes – NASA







