Mars Global Localization Pinpoints Perseverance’s Location
NASA/JPL-Caltech
Description
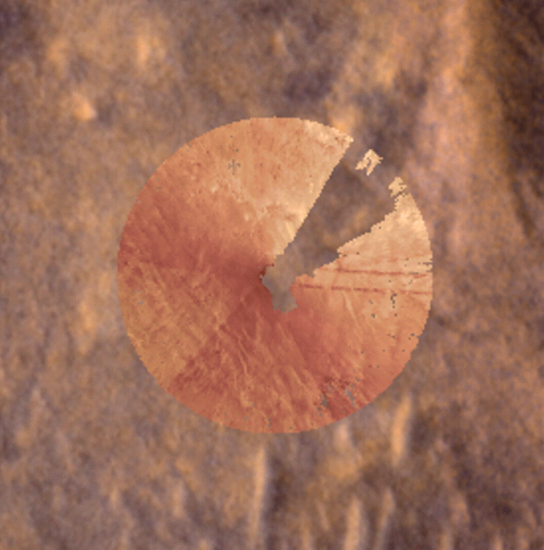
These images were part of the first successful use of a new technology called Mars Global Localization, developed at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Using its navigation cameras, NASA’s Perseverance captured a 360-degree view of the surrounding terrain that was matched to orbital imagery, enabling the rover to pinpoint its location on Mars on Feb. 2, 2026, the 1,762nd day, or sol, of the mission. The navcam images were turned into an overhead view called an orthomosaic, forming a circle around the rover. In this animation, the orthomosaic is superimposed on the imagery from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Contrast and hue have been enhanced to increase visibility of terrain features, which align in the ground and orbital imagery.
The rover took the five stereo pairs of navcam images in this relatively featureless location, dubbed “Mala Mala,” an area on the rim of Jezero Crater. The blank area in the upper right of the orthomosaic is where the back of the rover blocked the cameras’ view of the surrounding landscape.
Mars Global Localization features an algorithm that rapidly compares panoramic navcam shots to MRO orbital imagery. Running on a powerful processor that Perseverance originally used to communicate with the now-retired Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, the algorithm takes about two minutes to pinpoint the rover’s location to within some 10 inches (25 centimeters).
Like NASA’s previous Mars rovers, Perseverance tracks its position using what’s called visual odometry, analyzing geologic features in camera images taken every few feet while accounting for wheel slippage. As tiny errors in the process add up over the course of each drive, the rover becomes increasingly unsure about its exact location. On long drives, the rover’s sense of its position can be off by more than 100 feet (up to 35 meters). Believing it could be too close to hazardous terrain, Perseverance may prematurely end its drive and wait for instructions from Earth.
After each drive comes to a halt, the rover sends a 360-degree panorama to Earth, where mapping experts match the imagery with shots from MRO. The team then sends the rover its location and instructions for its next drive. That process can take a day or more, but with Mars Global Localization, the rover can compare the images itself, determine its location, and roll ahead on its pre-planned route.
Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover. JPL also manages MRO for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington as part of its Mars Exploration Program portfolio.
The post Mars Global Localization Pinpoints Perseverance’s Location appeared first on NASA Science.











